Editing
Linting and Formatting Assignments
Assignments come configured with linting and formatting. Provided for you are the npm run lint, npm run lint:fix, and npm run format commands.
Linting
From Wikipedia on Lint:
Lint, or a linter, is a static code analysis tool used to flag programming errors, bugs, stylistic errors and suspicious constructs. The term originates from a Unix utility that examined C language source code.
Homework assignments may require that you do not have any linter warnings. To check your linter warnings, use the npm run lint command in a terminal. It will produce output detailing where and how your code could improve.
If you do not understand what the warning means, Googling its name may help ("@typescript-eslint/no-unused-vars").
Using the VSCode ESlint extension will bring these warnings into the editor visually. Allowing you to hover your cursor over them and interact with them.
The npm run lint:fix command will attempt to fix all the automatically fixable warnings. Such as using let for a variable that is never reassigned.
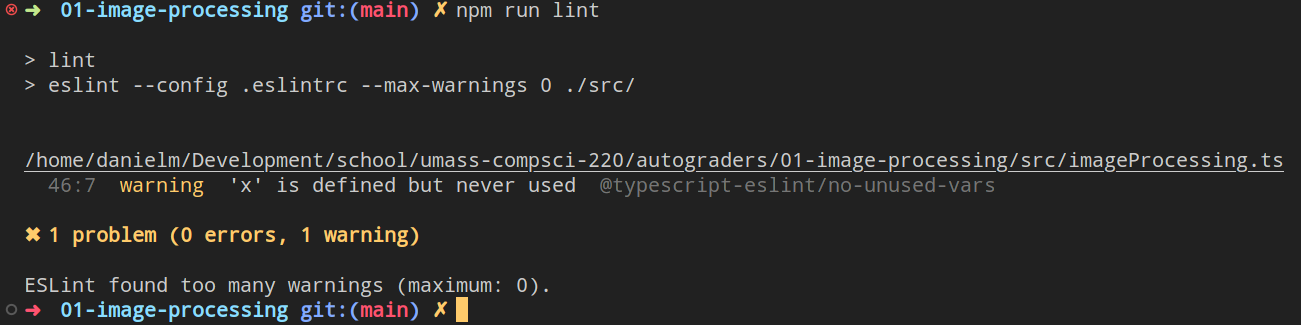
Above is some example output from running npm run lint. As you can see, on line 46, column 7, we are getting a warning because we define a variable x, but never use it.
Formatting
Formatting, i.e. the spacing and visual structure of your code, is handled before you build your final submission using the npm run format command. If you'd like, you can run this command periodically to format your code. Alternatively, you could configure VSCode to automatically format your code whenever you save your file.
Installing the Prettier extension in VSCode and adding the following to your settings.json (File -> Preferences -> Settings -> Open JSON (top right)) should configure it for you:
"[typescript]": {
"editor.defaultFormatter": "esbenp.prettier-vscode"
},
"editor.formatOnSave": true
Your code is formatted before you build your submission so it can be more easily read by course staff.